Quartz! Habits & Formations.
Quartz – The Master!
Types and habits.
I’m no expert on this subject but I do want to write about Quartz for a couple of reasons. I spend a lot of time talking about all the different types of quartz and their different habits (external shape) and formations. Another reason is that it’s my number one, all-time favourite crystal. It truly is the Master.
Types of Quartz
Quartz is a name given to well crystallized and compact forms of silica. Quartz is silicon dioxide. It has a hardness of 7, so it is extremely tough and durable. It belongs to the Trigonal crystal system and is one of the most abundant minerals on earth. There is Macrocrystalline Quartz and Microcrystalline Quartz. Macro is large and Micro is small. Macrocrystalline varieties of Quartz show small to large visible crystals or are made up of large intergrown crystals. Examples are Quartz/Rock crystal, Amethyst, Smoky Quartz, Citrine, Rose Quartz, Ametrine, Tigers Eye and Aventurine to name just a few. Microcrystalline varieties of Quartz are made up of minute crystal grains that are visible under a microscope. Examples are Carnelian, Agate, Chalcedony and Jasper to name just a few.
Habits and Formations
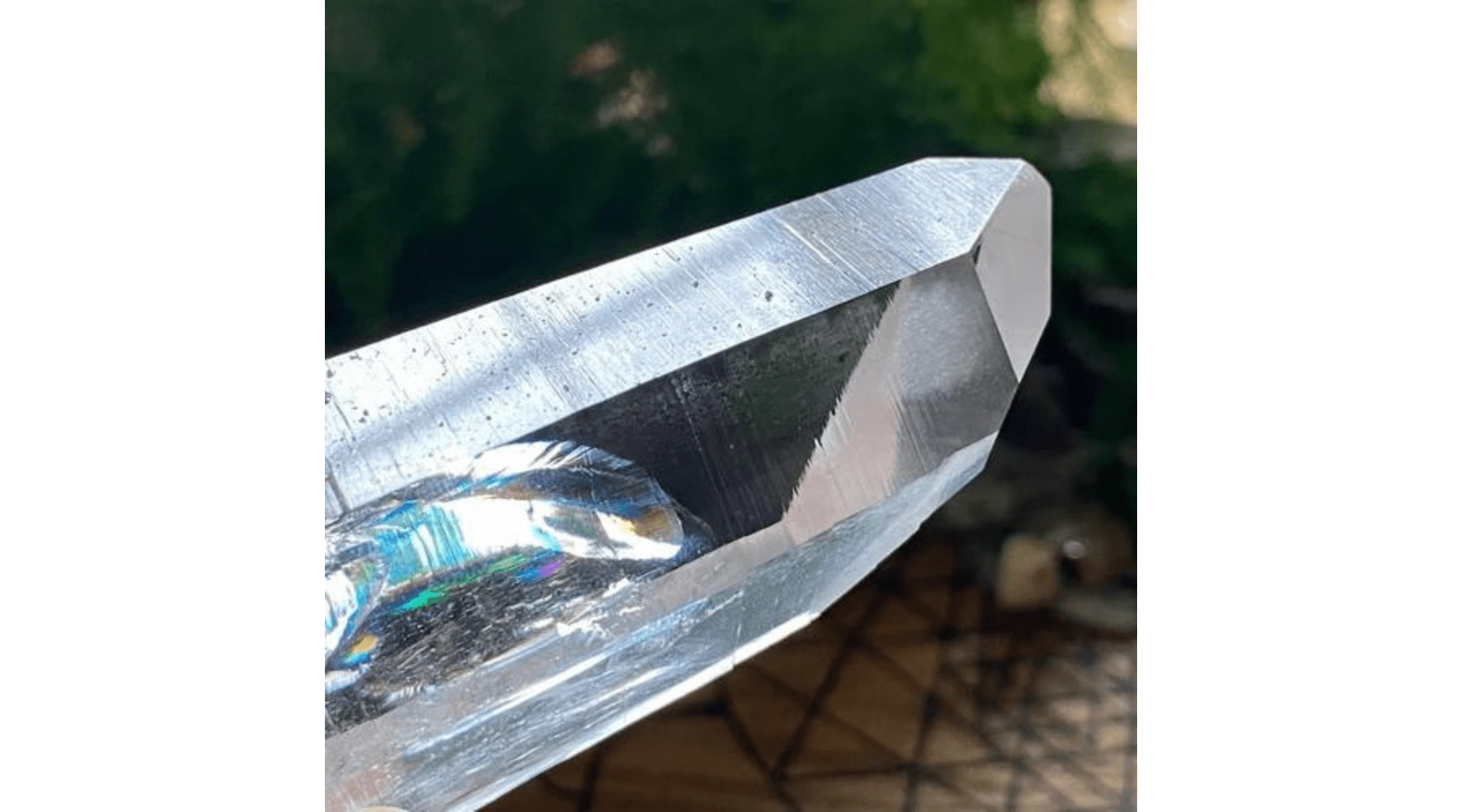
Habit is a word used to describe the external structure of a crystal, so what you actually see and feel. A formation refers to the growth and crystallisation of the crystal, so very similar to the crystal habit. To keep it simple, I'll be using the terms interchangeably to describe the overall look and appearance of the crystal. Many of the terms below refer to the crystals in a metaphysical sense but there are also the standard geological terms, such as the Muzo and Tessin habits. Most Lemurian quartz shows the classic Muzo habit and the Colombian Quartz often has both. There is one website I refer to often. Purely geological but it is written in an easy to understand way. It's a great source for all things Quartz. You can find it by clicking the link HERE
- Generator: A generator crystal has six equal-length sides, all coming together and meeting at the apex of the crystal.
- Laser: Usually long crystals that come to a tapered point/termination.
- Double-Terminated: A crystal that has two naturally terminated points at either end of the crystal.
- Tabby or Tabular: A flat crystal, a good example is a Faden Quartz
- Phantom: A phantom crystal is one that has internal layering, some refer to them as ghosts. It’s like there is a crystal inside a crystal.
- Self Healed: A self-healed crystal is where a crystal has become detached from its matrix, or broken away from another crystal, and the broken end has new crystal growth, resealing the damage.
- Faden: Faden Quartz has a fuzzy white line running through the centre of the crystal. They usually come in tabular formations.
- DOW: DOW crystals have three seven-sided faces with three triangular faces (7x3x7x3x7x3). DOW crystals are named after Janeann Dow and are often called Temple Heart Crystals.
- Isis: An Isis crystal has one larger face with five sides. The sides of the face are normally symmetrical.
- Channelling: Similar to a DOW but a Channeller has one seven-sided face with a three-sided face on the opposite side.
- Transmitter: A transmitter has two seven-sided faces either side of a three-sided face.
- Record Keepers: Record Keepers have triangular markings on the face of the crystal. These markings can be flat, sunken, raised and upside down (trigonic record keeper).
- Gwindel: Gwindel crystals are crystals that appear to have grown sideways.
- Cluster: Many crystals all together with fine determined points, often sitting on a matrix bed.
- Time Link/Window: A Time Link or Window crystal shows a parallelogram face or a diamond shape face in the apex of the crystal. They can appear on the left or right and can lean either side.
- Sceptre: A Sceptre crystal has a central rod that looks like it has been caped with another crystal.
- Enhydro: An Enhydro is a crystal that has trapped water inside, creating a moving bubble.
- Elestial: Elestial crystals have terminations all over the face of the main crystal.
- Bridge: A Bridge crystal is distinguished by showing crystals that are growing over, in or on the main crystal, forming a bridge-like appearance.
- Manifestation: A Manifestation crystal is a crystal that has a crystal growth inside the main crystal with no outside contact or entry point.
- Grounding Crystal: A Grounding crystal has a rare eight-sided main face.
- Key Release: A Key Release crystal is one that shows clear indentations that were left by another crystal.
- Soul Mate: Soul Mate crystals are where two crystals grow side by side, usually of a similar size. Twin and Soul crystals are often referred to as the same.
- Twin Flame: Twin Flame crystals are where two crystals are joined together, usually at the base, unlike the Soul Mate crystals that grow side by side. Twin and Soul crystals are often referred to as the same.
- Tessin habit: A crystal that gets continually smaller towards the tip, like the lasers. Colombian Quartz is a fine example.
- Muzo habit: Three-sided crystals, coming together towards the tip, forming a blade-like side. Good examples are Colombian, Brazilian Lemurian Quartz and Brandberg quartz.
Piezoelectricity
Did you know that Quartz is Piezoelectric? Piezoelectricity is an electric charge that accumulates in certain solid materials (quartz crystal) in response to applied mechanical stress. The word piezoelectricity means electricity resulting from pressure and unseen heat. Quartz crystal exhibits the property of piezoelectricity, by which it can transform mechanical energy (e.g., pressure) into electromagnetic energy, and vice versa. This makes it useful in such devices as crystal radios, microphones, watches, radio transmitters, etc.
How do Quartz watches work?
A battery electrically powers an electronic integrated circuit (IC) consisting of transistors, resistors and capacitors on a silicon chip. The IC converts power into pulses which via conducting material vibrate the quartz. The quartz vibrates at a constant rate of 32,768hz. The high frequency keeps the accuracy. The vibration pulse from the quartz returns to the IC where the IC converts the pulse into a reduced signal. (Mel V – Jacobs Jewellers).
Rock Crystal – Quartz
Clear Quartz is sometimes called ‘Rock Crystal,’ The name comes from the Greek for ‘ice’ and some of the ancients believed that Quartz crystal was water frozen so hard it could never thaw. Clear Quartz has long been the subject of spiritual beliefs and folklore. The Japanese called clear Quartz ‘the perfect jewel’, and viewed it as a symbol of infinite space, purity, perseverance and patience. Indigenous cultures in both North America and Burma have believed clear Quartzes to be living entities and presented them with food as ritual offerings. Crystal balls brought back by the Crusaders were said to possess magical powers. In Scotland and Ireland, spheres of rock crystal were long used to cure diseases in cattle. In past cultures of Central and South America, Quartz crystals carved into the shapes of human skulls were venerated as powerful religious objects—the dwellings of deceased ancestors or gods. In a remarkable coincidence or synchronicity, aboriginal tribes in both Australia and South America describe in their creation myths the image of the ‘cosmic serpent,’ progenitor of all life, being led and guided by a Quartz crystal. (The Book of Stones, Revised Edition).
This page is still work in progress, I will add more when time permits.